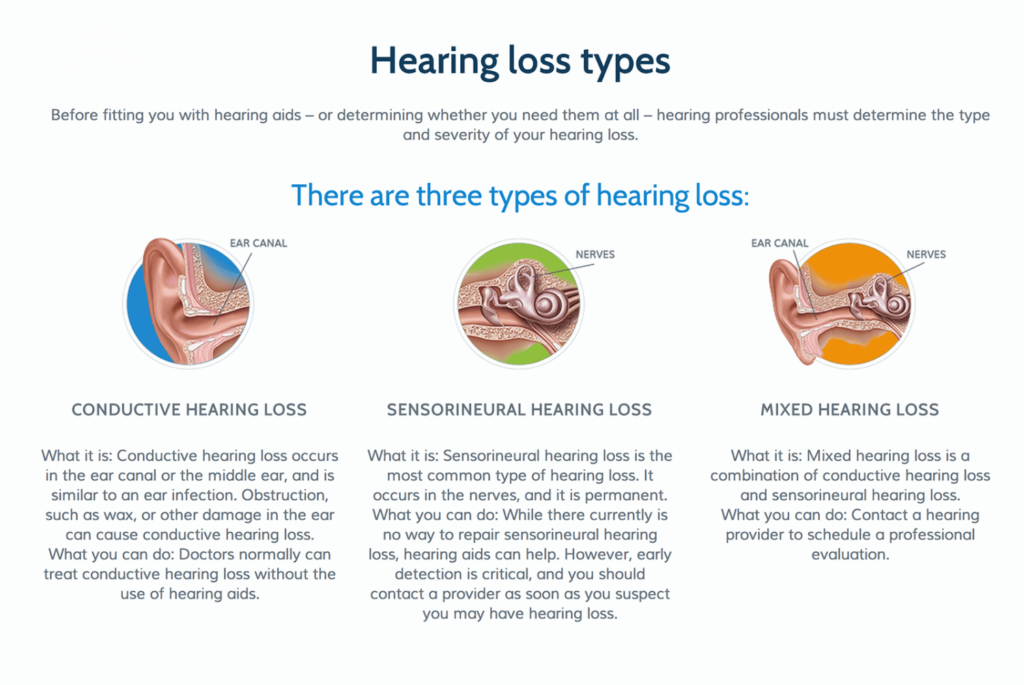
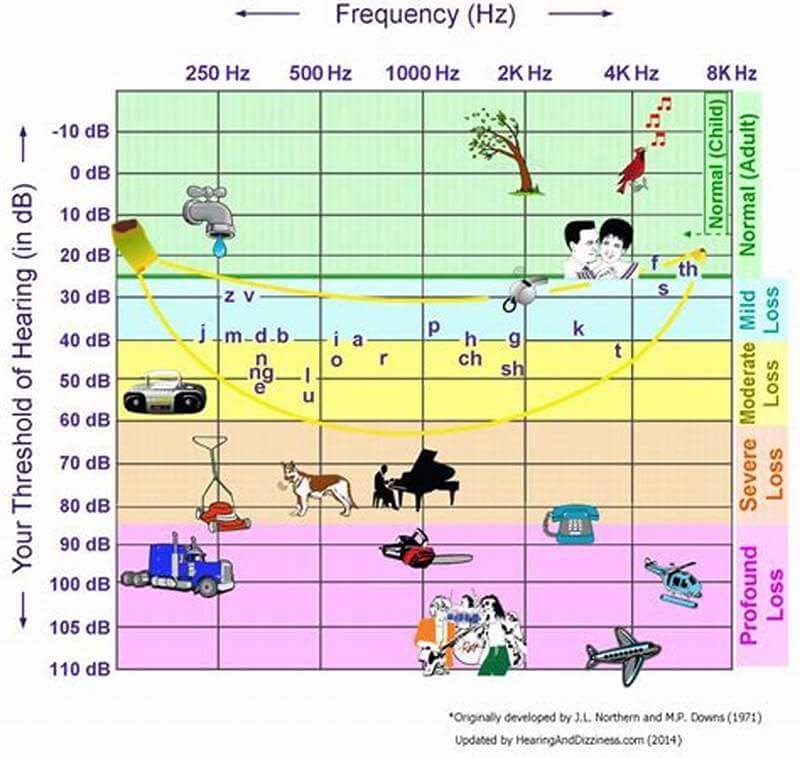
Hearing loss in adults is usually slow progressing. Most people with a hearing loss do not even complain of an active problem in hearing. Their primary concern remains in difficulty understanding words due to selective hearing loss for some sounds.
With the help of known context and focusing on the conversation, understanding of word becomes easy. At other times sentences may have to be repeated a few times before one may understand the meaning. An Untreated hearing loss has been linked with Alzheimer’s Disease, Dementia, Tinnitus in the elderly, apart from having an increased risk of falls, diabetes, depression, anxiety and social aloofness.
Therefore, one must get regular Hearing Check-ups, especially for a senior Citizen, to detect the early signs of hearing loss and give the right solution timely.